Backend Developer Roadmap 2025 - Complete Guide from Beginner to Senior Architect
Backend Developer Roadmap 2025: Complete Guide from Beginner to Senior Architect
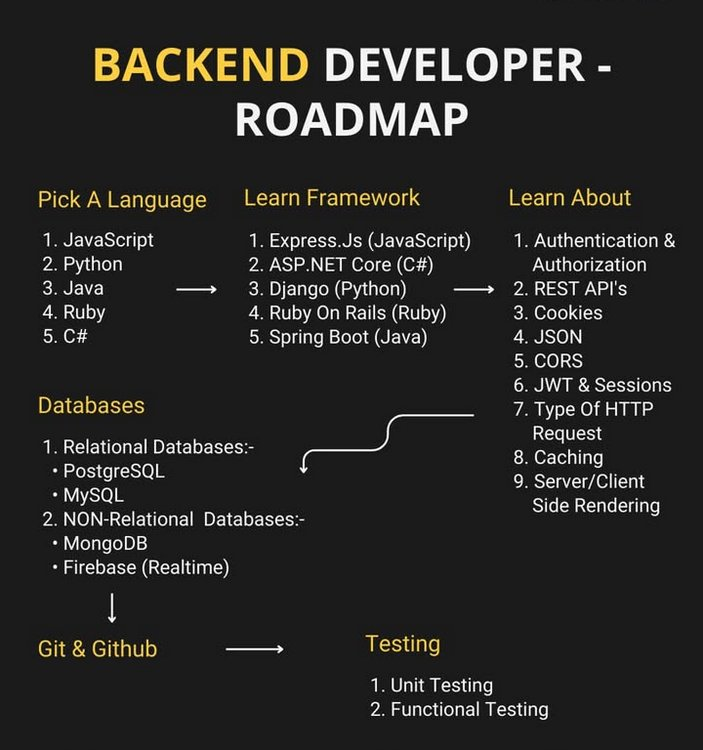
Backend development is the "engine" of internet applications, responsible for data processing, business logic, and interaction with frontend and databases. Many beginners get lost when facing the vast technology stack. This article will provide you with a complete learning path from beginner to senior backend engineer, based on the classic Backend Developer Roadmap and combined with 2025's latest technology trends and practical project experience.
This guide covers:
- Comparison and selection advice for 7 mainstream backend programming languages
- In-depth analysis of enterprise-level backend frameworks
- Complete database technology stack learning path
- REST API design best practices
- Core skills including authentication, authorization, caching, testing
- Career progression roadmap from junior to architect
1. Choose a Backend Language
Language is the entry point, and different languages have their own ecosystems and applicable scenarios. Common choices include:
- JavaScript (Node.js)
Suitable for rapid service construction, with a huge ecosystem (NPM), especially friendly for frontend-to-backend transitions. - Python
Simple syntax, rich scientific computing and AI libraries, commonly uses Django/Flask for web development. - Java
The backbone of enterprise-level backend, Spring Boot is the de facto standard. - Ruby
Ruby on Rails was once the first choice for startups, emphasizing "convention over configuration". - C# (.NET Core)
Powerful framework in Microsoft ecosystem, with increasingly complete cross-platform support.
Recommendation: Beginners can choose languages based on career planning. If you prefer startups and rapid development, choose JavaScript/Python; if you lean towards large enterprises or financial systems, Java/C# have more advantages.
2. Learn Backend Frameworks
Frameworks provide mature architectural patterns and development standards, allowing you to upgrade from "writing logic" to "writing systems":
- Express.js (JavaScript): Lightweight and flexible, the most popular Node.js framework.
- ASP.NET Core (C#): Microsoft's flagship with excellent performance.
- Django (Python): Built-in ORM, admin backend, security mechanisms, very suitable for full-stack development.
- Ruby on Rails (Ruby): High development efficiency, friendly community atmosphere.
- Spring Boot (Java): First choice for enterprise-level backend, supports microservice architecture.
The focus of framework learning is not only "how to write code", but also understanding the design concepts, such as MVC pattern, dependency injection, middleware mechanism.
3. Core Knowledge Points
After mastering languages and frameworks, you need to deeply understand backend core concepts:
Authentication & Authorization
- Authentication: Confirm user identity (such as login).
- Authorization: Control what users can do (such as permission management).
Common methods include Session, JWT, OAuth2.
REST API Design
- Follow resource-based URIs (such as
/users/123). - Use standard HTTP verbs (GET/POST/PUT/DELETE).
- Return unified JSON response structure.
- Follow resource-based URIs (such as
Cookies & Session
- Cookie: Small data stored on the browser side.
- Session: Session data stored on the server side.
- JWT (JSON Web Token) is a stateless alternative.
JSON and Data Interaction
- JSON is the most common data exchange format between backend and frontend.
- Familiar with serialization/deserialization.
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing)
Understand browser security policies and master how to configure cross-origin requests.Caching Mechanisms
- Server-side caching (Redis, Memcached).
- Client-side caching (HTTP cache headers, ETag).
Caching is key to performance optimization.
Rendering Modes
- SSR (Server-Side Rendering): SEO friendly.
- CSR (Client-Side Rendering): Smooth user experience.
- Hybrid solutions: Frameworks like Next.js support both.
4. Databases
Databases are the core of backend, commonly divided into relational and non-relational:
- Relational Databases (PostgreSQL, MySQL)
Suitable for transactional systems, such as e-commerce and finance. - Non-relational Databases (MongoDB, Firebase Realtime)
Suitable for high-concurrency applications with flexible data structures, such as social media and real-time chat.
Learning focus:
- SQL statements (queries, joins, transactions)
- Data modeling (normalization and denormalization)
- Indexing and performance optimization
5. Version Control and Collaboration
Git & GitHub are essential skills for modern development:
- Familiar with branching models (Git Flow / trunk-based development).
- Master common commands:
clone,commit,merge,rebase. - Use Pull Requests for code review.
6. Testing and Quality Assurance
Backend development doesn't end with writing logic; testing is key to ensuring system robustness:
Unit Testing
- Smallest test units for functions/modules.
- Tools: JUnit (Java), pytest (Python), Jest (JS).
Functional Testing
- Simulate user scenarios for testing, ensuring functions work as expected.
- Can be combined with API testing tools (Postman, Swagger).
7. Summary and Advanced Directions
The learning roadmap can be roughly divided into four stages:
- Beginner: Choose language + framework, master basic syntax and project setup.
- Intermediate: Deep dive into API design, database operations, authentication and caching.
- Engineering: Master Git, testing, CI/CD processes.
- Advanced: Deep dive into architectural design (microservices, message queues, distributed systems).
Backend development is not just about writing code, but understanding system performance, security, and scalability. By mastering the knowledge points in the Roadmap, you will have the ability to develop a complete backend system from scratch.